Python Learning Guide for Developers
By: Tauseef Fayyaz
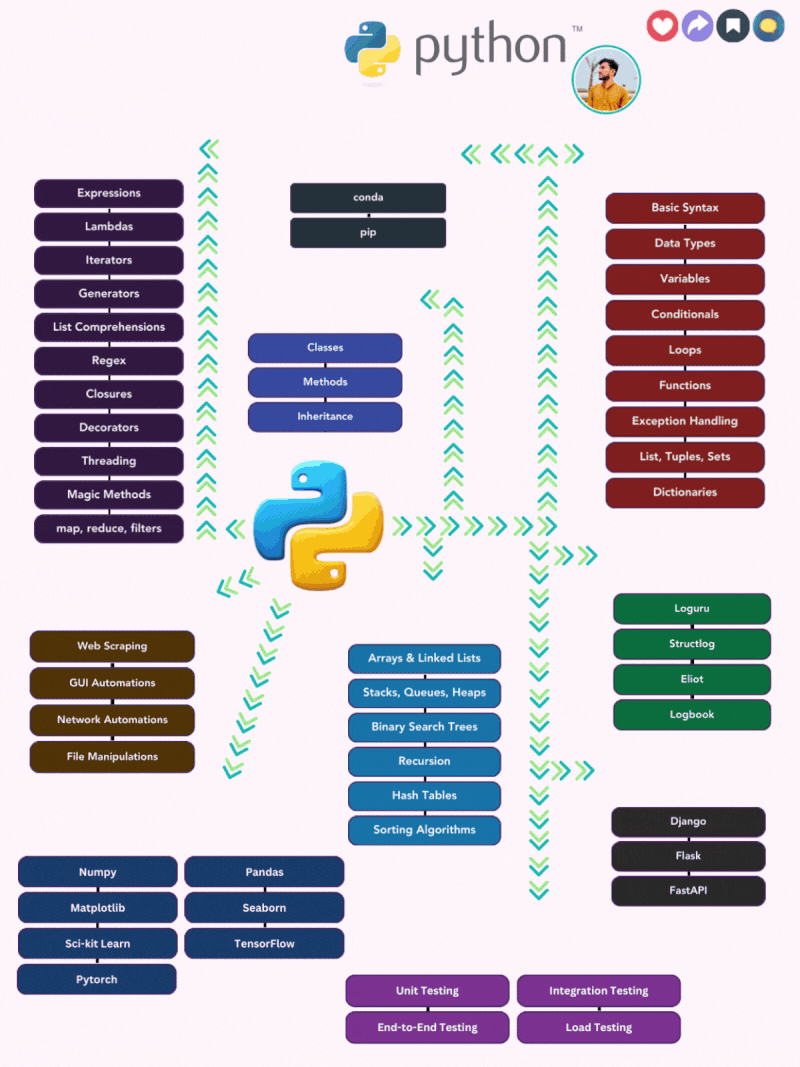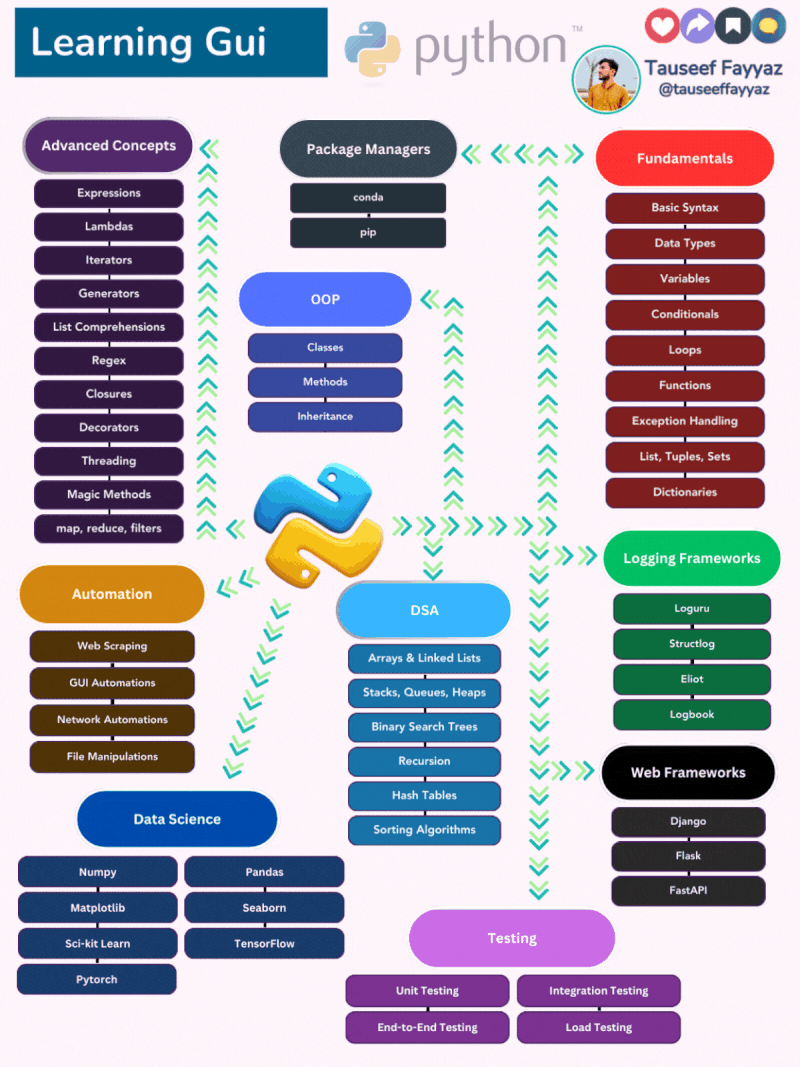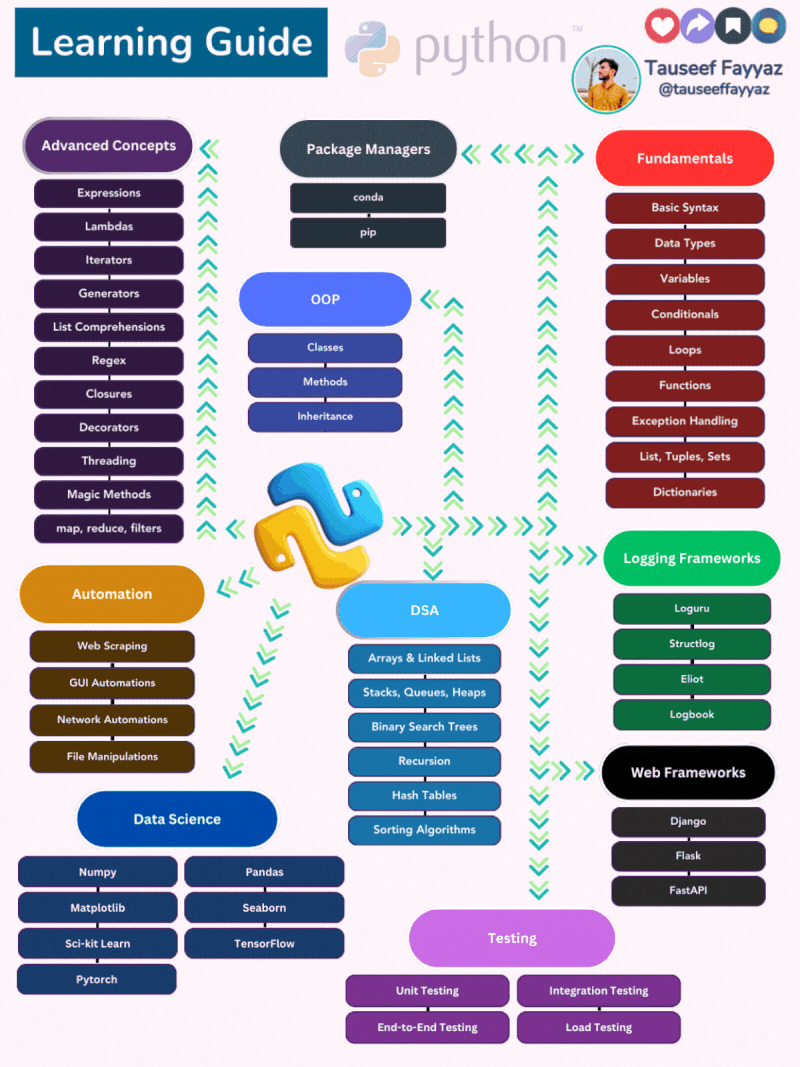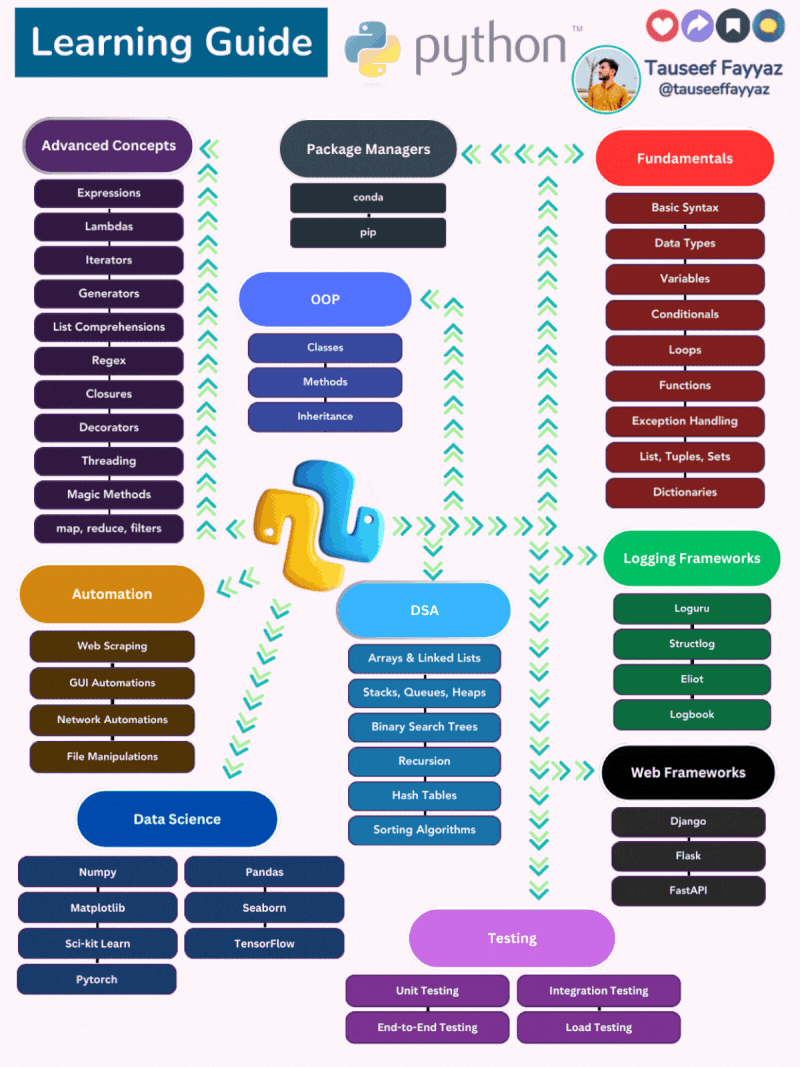
𝐏𝐲𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐧: 𝐋𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐧𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐆𝐮𝐢𝐝𝐞 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐃𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐥𝐨𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐬 😎
𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐦𝐦𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐅𝐮𝐧𝐝𝐚𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐥𝐬: The foundation of programming in Python, encompassing basic concepts like syntax, data types, variables, control flow, functions, error handling, and fundamental data structures.
𝐎𝐛𝐣𝐞𝐜𝐭-𝐎𝐫𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐝 𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐦𝐦𝐢𝐧𝐠 (𝐎𝐎𝐏): A paradigm for structuring code where objects encapsulate data and behavior, employing classes, methods, inheritance, and polymorphism to create modular and reusable software.
𝐃𝐚𝐭𝐚 𝐒𝐭𝐫𝐮𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐀𝐥𝐠𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐡𝐦𝐬 (𝐃𝐒𝐀): The building blocks of efficient data storage and manipulation, encompassing various data structures like arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, heaps, binary search trees, and hash tables, along with fundamental algorithms like recursion and sorting.
𝐀𝐝𝐯𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞𝐝 𝐏𝐲𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐧 𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐜𝐞𝐩𝐭𝐬: Deeper exploration of Python's capabilities, delving into expressions, lambdas, iterators, generators, list comprehensions, regex, closures, decorators, threading, magic methods, and higher-order functions for more sophisticated programming solutions.
𝐏𝐚𝐜𝐤𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐌𝐚𝐧𝐚𝐠𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭: The tools and techniques for managing Python packages, including conda and pip, enabling efficient installation, organization, and updating of external libraries.
𝐖𝐞𝐛 𝐅𝐫𝐚𝐦𝐞𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐤𝐬: Frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI that streamline web development in Python, providing robust frameworks for building dynamic web applications and APIs.
𝐀𝐮𝐭𝐨𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧: Utilizing Python to automate tasks, including web scraping, GUI automation, network automation, and file manipulations, enhancing productivity and streamlining repetitive processes.
𝐃𝐚𝐭𝐚 𝐒𝐜𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐞: The toolkit for data analysis and machine learning, encompassing NumPy, Matplotlib, Pandas, Seaborn, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch, enabling data exploration, visualization, modeling, and prediction.
𝐋𝐨𝐠𝐠𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐅𝐫𝐚𝐦𝐞𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐤𝐬: Tools like Loguru, Structlog, and Eliot for effectively capturing, formatting, and managing log data in Python applications, facilitating debugging, monitoring, and performance analysis.
𝐓𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠: Ensuring software quality and reliability through various testing approaches, including unit testing, end-to-end testing, integration testing, and load testing, identifying and resolving defects to maintain a robust and reliable codebase.
𝐏𝐲𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐧'𝐬 𝐩𝐨𝐩𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐰𝐢𝐝𝐞𝐬𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐝 𝐚𝐝𝐨𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐚𝐜𝐫𝐨𝐬𝐬 𝐢𝐧𝐝𝐮𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐢𝐞𝐬 𝐦𝐚𝐤𝐞 𝐢𝐭 𝐚 𝐯𝐚𝐥𝐮𝐚𝐛𝐥𝐞 𝐬𝐤𝐢𝐥𝐥 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐜𝐚𝐫𝐞𝐞𝐫 𝐚𝐝𝐯𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦-𝐬𝐨𝐥𝐯𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐢𝐧 𝐭𝐨𝐝𝐚𝐲'𝐬 𝐭𝐞𝐜𝐡𝐧𝐨𝐥𝐨𝐠𝐲-𝐝𝐫𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐧 𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐥𝐝.